Overview
1. Database
The underlaying graph structure is very flexible and easy to extend. Beside creating new nodes (entities) and relationships, it is also possible to extend the existing ones for your application. The following sections focus on this option.
1.1. Extending nodes
All nodes (Scenarios, Locations, Videos, ) have own properties. You can easily extend them with your own. If you have a new entity, for example: Users, which would bring own properties (for example: username, password, first_name, last_name, email_address), it is recommended to introduce a new node. With the help of a new relationship (for example: -[HAS_ACCESS]->) between a User and a Scenario, you would have built a simple authorization concept.
1.2. Extending relationships
All relationships can be weighted. In the example graph the property weight in the -[CONNECTED_TO]-> relationship has the value 1.0 to demonstrate this concept. This property could also be used or renamed to travel-minutes, which could then contain the minutes to go from one Location to another. For your application, you can simply extend the weights inside the relationships, they are fully customizable. Another example is the -[EMBEDDED_IN]-> relationship, between an and a Video. All settings of the translation, rotation and scaling are saved inside the -[EMBEDDED_IN]-> relationship, so a can used multiple times in different positions or different Videos, without duplicating an object.
2. REST-API
The CREATOR, as well as the VIEWER and REMOTE CONTROL, are using internally an REST-API to request and retrieve the data.
2.1. Postman
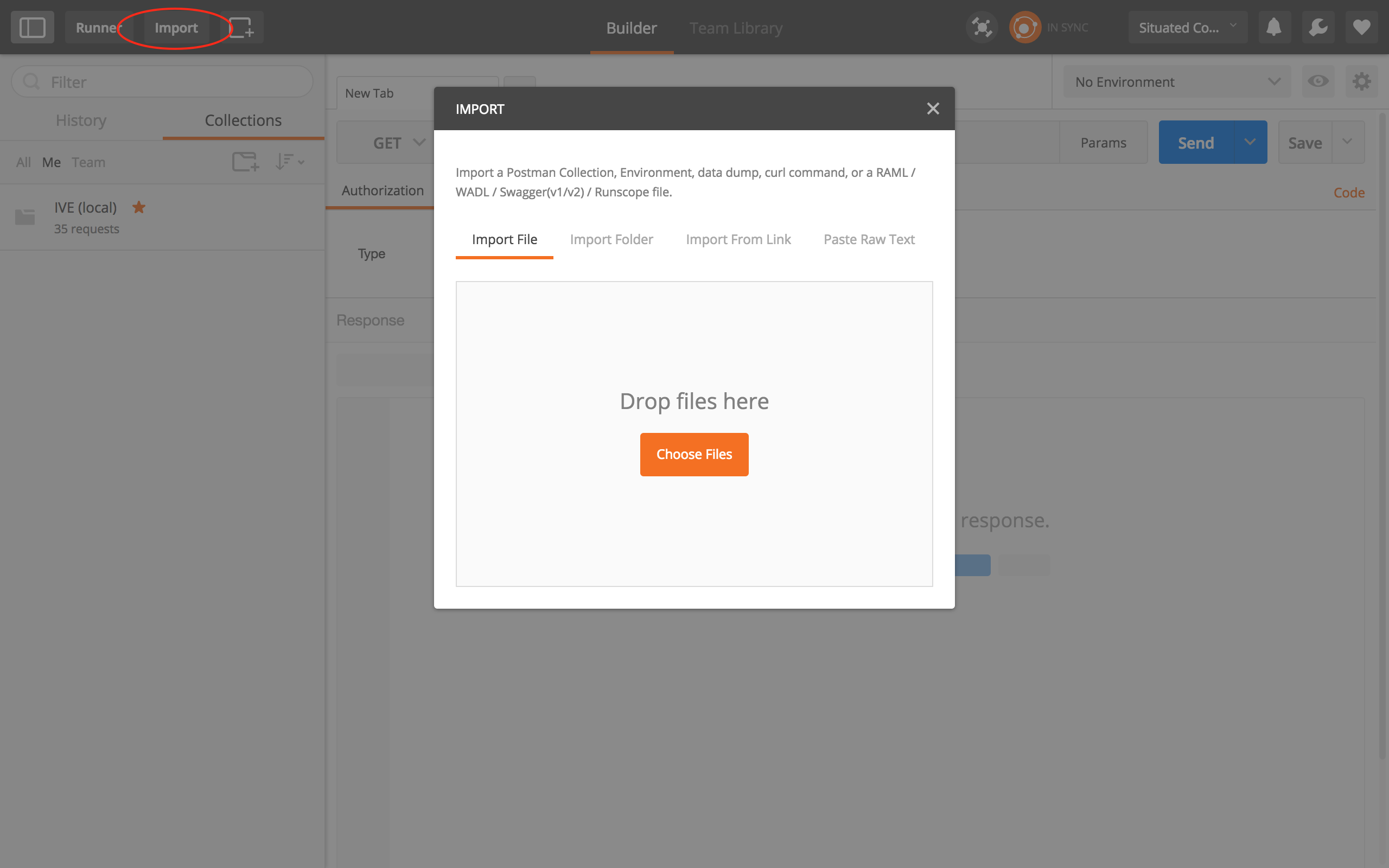
All data can be accessed by a REST-API. You can easily test out the endpoints with the program Postman. Install it as a client or as an Google Chrome extension.
In the folder /rest/* inside the repository, you can find two files, which can be imported to Postman. Import one of these files into Postman, like in the picture below or use the following button to download it automatically:
2.2. Endpoints
- Base-url:
/api/* - Headers:
Content-Type: application/jsonfor the body of POST and PUT requestsAuthorization: Bearer <TOKEN>for protected endpoints
| Method | Endpoint | Authentication | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST | /login |
||
| GET | /scenarios |
||
| POST | /scenarios |
||
| DELETE | /scenarios |
||
| GET | /scenarios/:scenario_id |
||
| PUT | /scenarios/:scenario_id |
||
| DELETE | /scenarios/:scenario_id |
||
| GET | /locations |
||
| POST | /locations |
||
| DELETE | /locations |
||
| GET | /locations/:location_id |
||
| PUT | /locations/:location_id |
||
| DELETE | /locations/:location_id |
||
| GET | /locations/:location_id/locations |
||
| GET | /scenarios/:scenario_id/locations |
||
| GET | /videos |
||
| POST | /videos |
||
| DELETE | /videos |
||
| GET | /videos/:video_id |
||
| PUT | /videos/:video_id |
||
| DELETE | /videos/:video_id |
||
| GET | /locations/:location_id/videos |
||
| GET | /scenarios/:scenario_id/locations |
||
| GET | /overlays |
||
| POST | /overlays |
||
| DELETE | /overlays |
||
| GET | /overlays/:overlay_id |
||
| PUT | /overlays/:overlay_id |
||
| DELETE | /overlays/:overlay_id |
||
| GET | /videos/:video_id/overlays |
||
| GET | /scenarios/:scenario_id/overlays |
||
| GET | /relationship/belongs_to/:label |
||
| GET | /relationship/connected_to |
||
| GET | /relationship/embedded_in |
||
| GET | /relationship/has_parent_location |
||
| GET | /relationship/recorded_at |
||
| POST | /relationship/belongs_to/:label |
||
| POST | /relationship/connected_to |
||
| POST | /relationship/embedded_in |
||
| POST | /relationship/has_parent_location |
||
| POST | /relationship/recorded_at |
||
| GET | /relationship/belongs_to/:relationship_id/:label |
||
| GET | /relationship/connected_to/:relationship_id |
||
| GET | /relationship/embedded_in/:relationship_id |
||
| GET | /relationship/has_parent_location/:relationship_id |
||
| GET | /relationship/recorded_at/:relationship_id |
||
| PUT | /relationship/belongs_to/:relationship_id/:label |
||
| PUT | /relationship/connected_to/:relationship_id |
||
| PUT | /relationship/embedded_in/:relationship_id |
||
| PUT | /relationship/has_parent_location/:relationship_id |
||
| PUT | /relationship/recorded_at/:relationship_id |
||
| DELETE | /relationships/:relationship_id |
||
| GET or DELETE | /reset |
||
| GET | /handlers/set/scenario/:scenario_id |
||
| GET | /handlers/set/location/:location_id' |
||
| GET | /handlers/set/video/:video_id |
3. Websockets
| Endpoint | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
/set/scenario |
{ "scenario_id": 1 } |
Set the scenario inside the VIEWER |
/set/location |
{ "location_id": 2 } |
Set the (start-) location inside the VIEWER |
/set/video |
{ "video_id": 3 } |
Set (change) the current video inside the VIEWER |
/toggle/overlay |
{ "overlay_id": 4 } |
Show or hide the current overlay inside the VIEWER |
4. Extensions
4.1. Voice control system
The IVE was extended by Nicholas Schiestel with a voice control system as part of his bachelor thesis. The following image shows the basic architecture of the implementation.
The voice control system uses the expressions <-> intents approach. This means a user can give a variation of voice commands (expressions), for example: “Go left” or “Turn left”. But these commands have all the same meaning, for example: “navigate_left”, which allows to aggregate them into a single intent. If one of those expression is matched during the voice recognition phase, the identified intent is sent back from the voice recognition system (Wit.Ai) to the IVE. Based on this idea multiple intents, which different meanings (for example: “go_left”, “go_right”, etc.) can be used to build a simple navigation system for the IVE. The property intents inside the -[CONNECTED_TO]-> relationship is an array, which contains all available intents for this relationship. Based on this, all out-going -[CONNECTED_TO]-> relationships of the current Location can be searched for the intent name, the voice recognition system had identified. If the intent can be found inside the relationships, the system can navigate to the connected Location. One requirement for this simple search algorithm it that all intent names have to be unique.